FOCUSED ON CHARACTER
HOW WE SHAPE CHARACTER CURRICULUM IN THE CHESAPEAKE REGION
Our 2017 season brought back perennial school partners like Episcopal High School for their 20th year of Outward Bound expeditions. It also brought unique opportunities to serve groups of students from across the region and country - such as Tundra Women’s Coalition, Laalot, and Girl Scouts of Gulf Coast Florida. We embarked on our second year of spring break expeditions that combined United States Naval Academy midshipmen and military veterans on a week-long challenge along the Appalachian Trail.
Our outreach efforts within the Baltimore community strengthened with growing support and integration of our Character Curriculum. Thanks to our community of donors, we were able to make Outward Bound possible for 87% of the students we served.
Our redesigned Professional Development program for Educators brought even more character education opportunities to students in classrooms, extending their lessons far beyond our programs.

A REPORT CARD FOR LIFE
HELPING SCHOOLS AND STUDENTS UNDERSTAND THE IMPACT OF CHARACTER EDUCATION
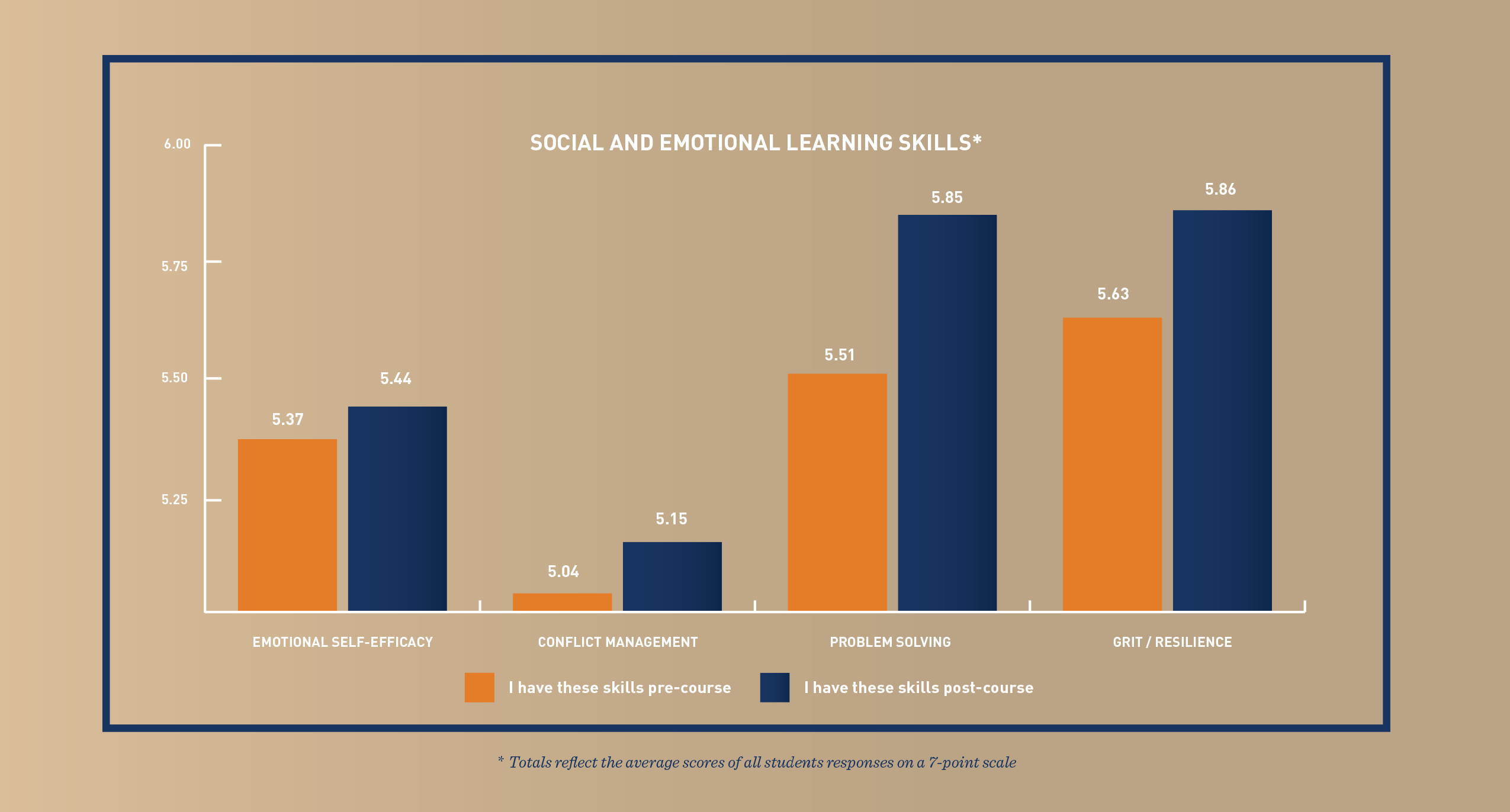
Since 2016, we’ve been using a survey tool developed by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health to measure specific growth in the social-emotional learning skills of our students (see right for descriptions of each). Participants on our five-day or longer expeditions complete the survey before and after their course. Below is a cumulative look at the improvements made over the entire 2017 season.
SOCIAL-EMOTIONAL LEARNING SKILLS
CONFLICT MANAGEMENT
Enhancing abilities to manage conflict non-violently via effective communication and conflict resolution and to understand the importance of constructive conflict management are a necessary component of reducing youth violence.
EMOTIONAL SELF-EFFICACY
The ability to manage emotions in a constructive manner helps young people react to stress and challenge in healthy, non-violent ways.
GRIT / PERSEVERANCE
Maintaining intentions and persisting in the face of challenge is a key non-cognitive skill associated with the success of youth who grow up in adverse conditions.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Having confidence in his or her ability to address problems and utilize problem solving strategies enhances the likelihood an adolescent will be able to successfully navigate social and academic challenges.